Dams l السدود
Dams l السدود
CONSTRUCTION OF A DAM EMBANKMENT WITH NONSTATIONARY QUEUES
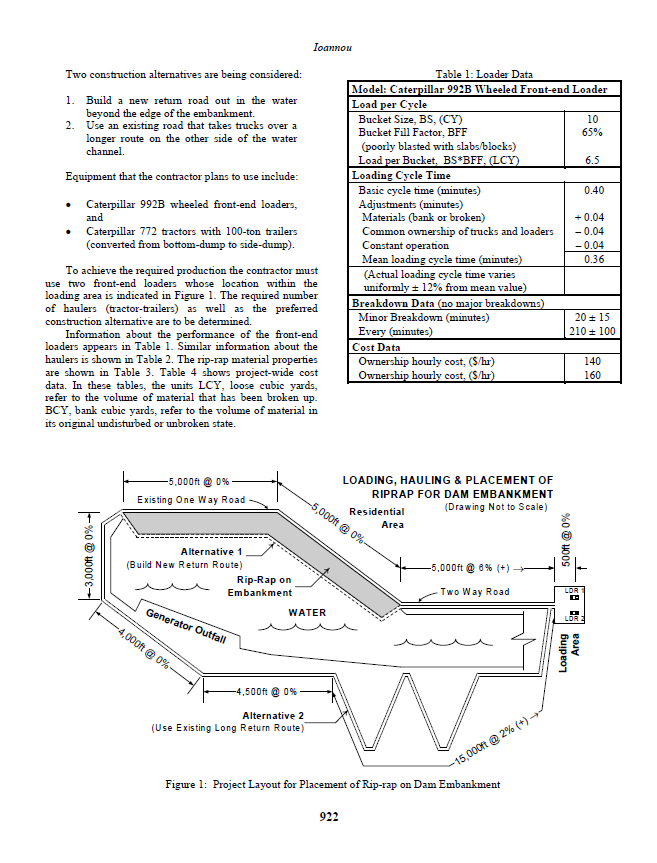
This paper presents the simulation model for a project involving the haulage and placement of rip-rap for the construction of a dam to illustrate how traffic-related queues are created at locations determined dynamically at simulation runtime. This example also investigates the formation of moving queues of equipment that cannot pass each and travel together like a procession or a convoy. The
solution to this problem is outlined conceptually using the activity-scanning modeling paradigm and is described in detail using a simulation model developed in STROBOSCOPE.

Construction Control for Earth
The safety and satisfactory performance of earth and rockfill dams require competent and adequate supervision, careful inspection, and control testing. It is the responsibility of the Resident Engineer to bring to the attention of the Engineering Division any design or construction detail not adequately covered by the plans and specifications. The Resident Engineer must provide the field supervision and control required to accomplish the intent of the plans and specifications. The resident engineer must also coordinate the work with design engineers and provide guidance to the contractor if unexpected conditions are discovered during construction.

General Design and Construction Considerations for Earth and Rock-Fill Dams
This manual presents fundamental principles underlying the design and construction of earth and rock-fill dams. The general principles presented herein are also applicable to the design and construction of earth levees. The construction of earth dams by hydraulic means was curtailed in the 1940’s due to economic considerations and liquefaction concerns during earthquake loading and are not discussed herein.

Gravity Dam Design
Basically, gravity dams are solid concrete structures that maintain their stability against design loads from the geometric shape and the mass and strength of the concrete. Generally, they are constructed on a straight axis, but may be slightly curved or angled to accommodate the specific site conditions. Gravity dams typically consist of a non over flow section(s) and an overflow section or spillway.
The two general concrete construction methods for
concrete gravity dams are conventional placed mass concrete and RCC.
HYDRAULIC DESIGN OF LOCK CULVERT VALVES
The purpose of this manual is to present hydraulic design data on control valves for navigation lock filling and emptying systems

Hydraulic Design of Navigation Dams
This manual provides current guidance and
engineering procedures for the hydraulic design of navigation dams.

Hydraulic Design of Navigation Locks
This manual presents the results of research, design studies, and operation experience as guidance
for the hydraulic design of navigation locks.
SEEPAGE ANALYSIS AND CONTROL FOR DAMS
This manual presents the fundamental design principles and guidance concerning seepage considerations for design of new dams and the evaluation of existing projects

Instrumentation of Embankment Dams and Levees
This manual provides guidance to Corps of Engineers personnel who are responsible for
monitoring and analyzing embankment dams and levees.
- wasacademyAutodesk Revit Architecture Certified Professional Course4 HoursAll levels41 Lessons0 Quizzes0 StudentsFree
- wasacademyAutodesk Revit Structure Certified Professional Course4 HoursAll levels46 Lessons0 Quizzes0 StudentsFree
- wasacademyLearn Autodesk Revit Structure for Beginners& Professionals97 MinutesAll levels19 Lessons0 Quizzes1 StudentFree
- wasacademyLearn Revit®2021 Advanced with Upgraded Actual Projects3 HoursAll levels17 Lessons0 Quizzes0 StudentsFree